What is a Rick West Tarantula?
The term ‘Rick West Tarantula’ isn’t a specific species, but rather, this search query is likely referring to a type of tarantula or the general information related to tarantulas, possibly sought by someone named Rick West. Tarantulas are large, hairy spiders belonging to the Theraphosidae family. They are popular pets due to their relatively docile nature, interesting appearance, and manageable care requirements compared to other exotic pets. They are native to various regions worldwide, thriving in diverse habitats from tropical rainforests to arid deserts. Their size, coloration, and unique behaviors make them fascinating creatures to observe and care for. While ‘Rick West Tarantula’ is not a scientific classification, the information provided is about tarantulas in general, and can also satisfy this search query.
Origin and Habitat
Tarantulas are found in a wide range of habitats across the globe, primarily in tropical and subtropical regions. Their natural habitats include rainforests, grasslands, deserts, and even mountainous areas. The specific habitat preferences vary depending on the tarantula species. Some species are terrestrial, living in burrows they dig in the ground, while others are arboreal, inhabiting trees and shrubs. Understanding the origin and habitat of a tarantula is crucial for providing appropriate care in captivity. Replicating their natural environment, including temperature, humidity, and substrate, is essential for their health and well-being. This ensures that your tarantula thrives and exhibits its natural behaviors. Different species have adapted to various ecological niches, so research is vital when considering a specific species.
Physical Characteristics

Size and Appearance
Tarantulas exhibit a diverse range of sizes and appearances, varying significantly across different species. Generally, they are characterized by their large size, hairy bodies, and eight legs. Some species are relatively small, with a leg span of only a few inches, while others can grow to be quite large, with leg spans exceeding 10 inches. The body of a tarantula is divided into two main parts: the cephalothorax (fused head and thorax) and the abdomen. They possess chelicerae (mouthparts) with fangs, used for capturing prey and defense. Their bodies are covered in hairs, which serve various functions, including sensory perception and defense. These hairs can be urticating, causing irritation if they come into contact with skin. Their impressive size and unique physical features make them captivating creatures.
Color Variations
Color variations in tarantulas are incredibly diverse, adding to their appeal as exotic pets. The coloration of tarantulas ranges from earthy browns and blacks to vibrant blues, reds, oranges, and yellows. Some species display intricate patterns and markings on their bodies, adding to their visual interest. The color of a tarantula can be influenced by several factors, including genetics, habitat, and diet. The vibrant colors of some tarantula species often serve as camouflage or warning signals, while others blend seamlessly with their environment. These varied colors make each species unique, allowing owners to appreciate the beauty and diversity within the tarantula family. Proper lighting and care can also enhance and maintain the vibrancy of their colors in captivity.
Behavioral Traits

Temperament and Handling
The temperament of tarantulas varies significantly depending on the species and individual spider. Some tarantulas are known for being docile and relatively easy to handle, while others can be more defensive and prone to biting. It is essential to research the specific species’ temperament before attempting to handle it. Handling a tarantula should always be done with caution and respect. Avoid sudden movements and be mindful of the spider’s body language, such as posture and hair-flicking. Always support the tarantula’s body and legs, as they are delicate creatures. It is recommended to handle tarantulas as little as possible, as it can stress them out. Using a soft brush to gently coax the tarantula onto your hand or a surface can be a safer option.
Defensive Mechanisms
Tarantulas have developed several defensive mechanisms to protect themselves from predators. One of the most common defenses is the flicking of urticating hairs from their abdomen. These hairs, when contacted, cause skin irritation, deterring potential threats. Some tarantulas also possess the ability to bite, injecting venom as a defense mechanism. The potency of tarantula venom varies across species, but it is rarely life-threatening to humans. Tarantulas may also display aggressive postures, such as raising their front legs or displaying their fangs, as a warning. Understanding these defensive mechanisms is essential for handling tarantulas safely and recognizing signs of stress or aggression.
Diet and Feeding

Feeding Habits
Tarantulas are carnivorous creatures, feeding primarily on insects and other invertebrates. Their feeding habits involve capturing prey, injecting venom to immobilize it, and then consuming the softened tissue. The frequency of feeding depends on the tarantula’s age, size, and metabolism. Young tarantulas typically need to be fed more frequently than adults. They are opportunistic hunters, and their feeding behavior can be influenced by factors such as hunger level and environmental conditions. Observing your tarantula’s feeding habits helps you understand its needs and adjust its diet accordingly. A healthy tarantula will readily consume its prey. Ensuring a varied diet is important to provide all necessary nutrients.
Recommended Food
The diet of a tarantula should consist primarily of insects such as crickets, mealworms, roaches, and other commercially available feeder insects. It’s crucial to ensure that the insects are gut-loaded before feeding them to your tarantula. Gut-loading involves feeding the insects nutritious foods, such as vegetables and fruits, which will provide the tarantula with essential vitamins and minerals. You can also supplement the tarantula’s diet with occasional treats, such as pre-killed mice (for larger species only). The size of the prey should be appropriate for the tarantula’s size, and any uneaten food should be removed to prevent mold growth. Providing a varied diet will help keep your tarantula healthy and ensure they get the nutrients they need.
Nutrition Needs

Tarantulas require a balanced diet to maintain their health and thrive in captivity. In addition to insects, they also need access to fresh water at all times. Ensure that the water source is shallow and easily accessible to prevent drowning. Young and growing tarantulas require more frequent feeding compared to adult tarantulas. The nutritional needs of a tarantula are met through the insects they consume. Providing a diverse range of insects ensures that the tarantula receives a variety of nutrients, including protein, fats, and vitamins. Gut-loading the insects before feeding them to your tarantula significantly improves the nutritional value of their diet. This helps to ensure they get all the essential vitamins and minerals.
Lifespan and Life Cycle
Average Lifespan
The lifespan of a tarantula varies greatly depending on the species and sex. Female tarantulas typically live much longer than males. Some female tarantulas can live for over 20 years, while males often live only a few years after reaching maturity. Factors such as diet, environmental conditions, and overall care can also influence a tarantula’s lifespan. Creating a stable and suitable environment, along with a proper diet, are vital for a long and healthy life. Understanding the average lifespan of the species you own is crucial for responsible pet ownership. It allows you to prepare for the long-term care and commitment that comes with owning a tarantula.
Moulting Process
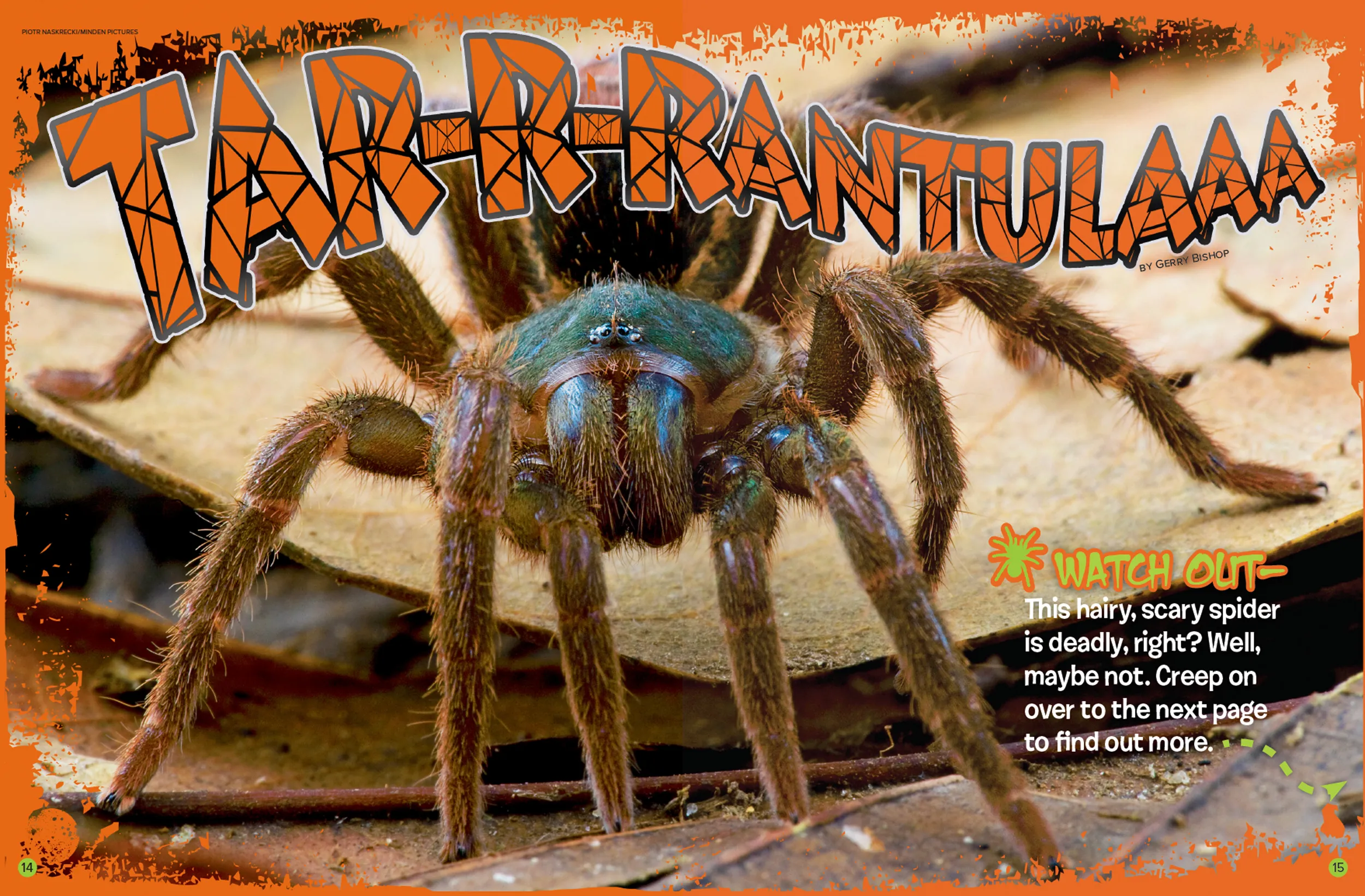

Moulting is a natural process where tarantulas shed their exoskeleton to allow for growth and renewal. During moulting, the tarantula will typically lie on its back, and the old exoskeleton will split, allowing the tarantula to emerge with a new, larger body. Moulting frequency depends on the tarantula’s age and growth rate; young tarantulas moult more often. Before moulting, tarantulas may stop eating and appear sluggish. It’s crucial not to disturb a tarantula during moulting, as they are very vulnerable during this process. After moulting, the tarantula’s new exoskeleton will be soft and delicate, and it will take a few days to harden. Provide a safe, undisturbed environment during this period.
Reproduction
Reproduction in tarantulas involves a complex process that begins with mating. Male tarantulas create a sperm web and transfer sperm to their pedipalps, specialized appendages near their mouth. They then seek out a mature female. The female will often signal her readiness for mating through pheromones. After mating, the female will lay eggs and create an egg sac, where the eggs develop. The number of eggs can vary widely depending on the species. The female tarantula will often guard the egg sac until the spiderlings hatch. Raising tarantulas involves careful management of environmental conditions and providing appropriate food sources. The process of breeding tarantulas should be done with expert knowledge and under controlled conditions.
Common Health Issues
Tarantulas are generally hardy creatures, but they can be susceptible to certain health issues. Common health problems include dehydration, injuries during moulting, and parasitic infections. Maintaining the proper humidity levels is crucial to prevent dehydration. Providing a shallow water dish and misting the enclosure can help maintain adequate humidity. Careful handling and a safe enclosure environment can minimize the risk of injuries. Parasitic infections can be prevented by providing clean food and water and maintaining a clean enclosure. Recognizing the signs of illness early on and seeking veterinary advice are essential for ensuring your tarantula’s health. Preventative measures, such as proper care and a balanced diet, can help prevent common health issues.
Preventive Care
Preventive care is crucial for maintaining a healthy tarantula. This includes providing a suitable enclosure, maintaining the appropriate temperature and humidity levels, and feeding them a balanced diet of appropriately sized insects. Regular cleaning of the enclosure is also essential to prevent the buildup of waste and the growth of mold. Monitoring your tarantula’s behavior and appearance can help you detect any potential health issues early. Providing hiding places and enrichment activities can reduce stress and promote their well-being. Proper preventive care can help ensure your tarantula lives a long and healthy life. This includes providing clean water, appropriate substrate, and a secure, well-ventilated enclosure.
Signs of Illness
Recognizing the signs of illness in tarantulas is important for timely intervention. Some common signs of illness include loss of appetite, lethargy, unusual posture, and changes in coloration. Difficulty moulting or failure to moult is also a sign of a problem. Other signs can include swelling or discharge from the mouth or fangs, and unusual changes in behavior, such as excessive hiding or irritability. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to consult with a veterinarian experienced in exotic animals. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the chances of a full recovery. Keeping a close eye on your tarantula and knowing the signs of illness can make a significant difference in their health.
Where to Find a Rick West Tarantula?
As ‘Rick West Tarantula’ is not a specific species, this section provides general guidance on where to find tarantulas for sale. Tarantulas can be purchased from reputable pet stores specializing in reptiles and exotic animals. You can also find tarantulas for sale from online retailers. It is essential to choose a reputable source. This ensures that you get a healthy tarantula and receive accurate information about its care. When purchasing a tarantula, make sure to research the species, its specific requirements, and any potential health issues. Also, make sure to check local laws and regulations regarding owning exotic pets. This research is vital for the health and well-being of your new pet and allows you to provide the proper care they need.
Responsible Ownership
Responsible ownership is essential for the ethical and humane care of tarantulas. This includes providing a suitable enclosure, maintaining the proper environmental conditions, and feeding them a balanced diet. Thoroughly research the specific species before acquiring a tarantula. This will help you understand its needs and ensure that you can provide proper care. Be prepared to make a long-term commitment, as tarantulas can live for many years. Proper care is a commitment. Always handle tarantulas with caution, and avoid handling them if they appear stressed or agitated. By providing a safe, enriching environment, you can ensure your tarantula thrives and lives a long, healthy life. Owning a tarantula can be a rewarding experience, provided you prioritize their well-being and understand the responsibility it entails.
