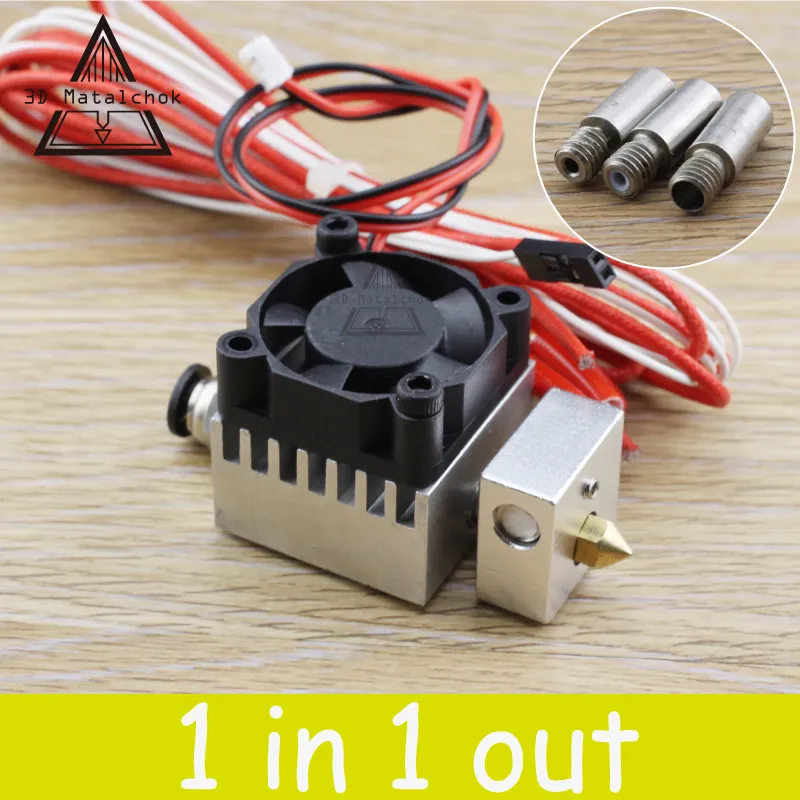
What is a Tarantula Extruder
A tarantula extruder is a specialized 3D printing component designed to melt and deposit filament, typically plastic, to build three-dimensional objects layer by layer. The ’tarantula’ in the name often refers to a specific model or design of 3D printer, and the extruder is a crucial part of the printing process. It precisely controls the flow of molten plastic, ensuring the accurate creation of complex shapes. Understanding the mechanics and functionality of an extruder is the initial stage for anyone looking to construct their own.
Benefits of a Tarantula Extruder
Building your own tarantula extruder presents several advantages over purchasing a pre-made one. Firstly, it can be a cost-effective solution, allowing you to save money by sourcing individual components. Moreover, it offers a high degree of customization. You can tailor the extruder’s design and specifications to meet your specific printing requirements and preferences. Assembling the extruder provides an in-depth understanding of its inner workings, empowering you to troubleshoot and maintain it efficiently. Customization options allow for use with different filament types or print at different resolutions.
How to Get Started
Embarking on the journey of building a tarantula extruder requires meticulous planning and preparation. This section will guide you through the initial steps, including material gathering and ensuring you have all the necessary tools. Before you start, research and familiarize yourself with the specific tarantula extruder design you intend to build. There are numerous open-source designs available online, each with its own set of requirements. Read through the instructions and gather the necessary information to make the building process more straightforward.
Gathering Materials
The success of your tarantula extruder build hinges on the quality and completeness of the materials you gather. Creating a detailed material list based on your chosen design is essential. The quality of the materials directly impacts the extruder’s performance and longevity. Take the time to select high-quality components from reputable suppliers. Ensure that all parts are compatible with each other and that you have enough of each item. Consider purchasing some extra components as spares in case of any unforeseen issues during the construction phase. Having backup parts can save a lot of time in the future.
Detailed Material List
Your material list should be incredibly detailed. Include all items needed for the extruder’s build. For example, include the hot end, which melts the filament, a thermistor to measure temperature, a heating element, and a nozzle to extrude the molten plastic. You’ll also need a stepper motor to drive the filament, a heatsink to dissipate heat, and various screws, nuts, and bolts for assembly. Consider the specific filament type you intend to use, as this may influence the material of the nozzle (e.g., stainless steel for standard filaments or hardened steel for abrasive filaments). Create a checklist as you gather each item, ensuring you have everything before starting the physical construction.
Tools You Will Need
Besides the materials, you will need a set of tools to assemble your tarantula extruder. These can range from basic hand tools to more specialized equipment. Essential tools include screwdrivers (both Phillips head and flathead), a set of Allen wrenches, pliers, wire strippers, and a multimeter for electrical testing. Depending on the design, you may also need a soldering iron, a drill, and possibly a 3D printer to print certain parts. Ensure that all of your tools are in good working condition and are suitable for the tasks involved. Consider having a well-lit workspace and a clean environment to avoid damaging the sensitive components.
The Construction Process
The construction of your tarantula extruder is a step-by-step process that requires patience and precision. Before starting the physical assembly, thoroughly review the design instructions, paying close attention to any specific recommendations or warnings. Organize your workspace to keep everything tidy and easily accessible. Be careful with the hot end and heating element; these components can get extremely hot during operation. Keep all the electrical components properly insulated to prevent any short circuits or damage. Regularly check your progress against the design documentation to identify potential issues early on.
Step-by-Step Guide
Follow the step-by-step instructions meticulously. Start by assembling the mechanical components, such as the hot end, heatsink, and extruder body. Ensure all screws are tightened securely but not over-tightened. Next, mount the stepper motor and connect it to the extruder. After the mechanical assembly, move on to the wiring and electronics. Connect the thermistor, heating element, and motor wires, following the provided wiring diagram. Double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and correctly wired. Carefully review the documentation to avoid any mistakes that could damage the components or compromise the extruder’s performance.
Wiring and Electronics
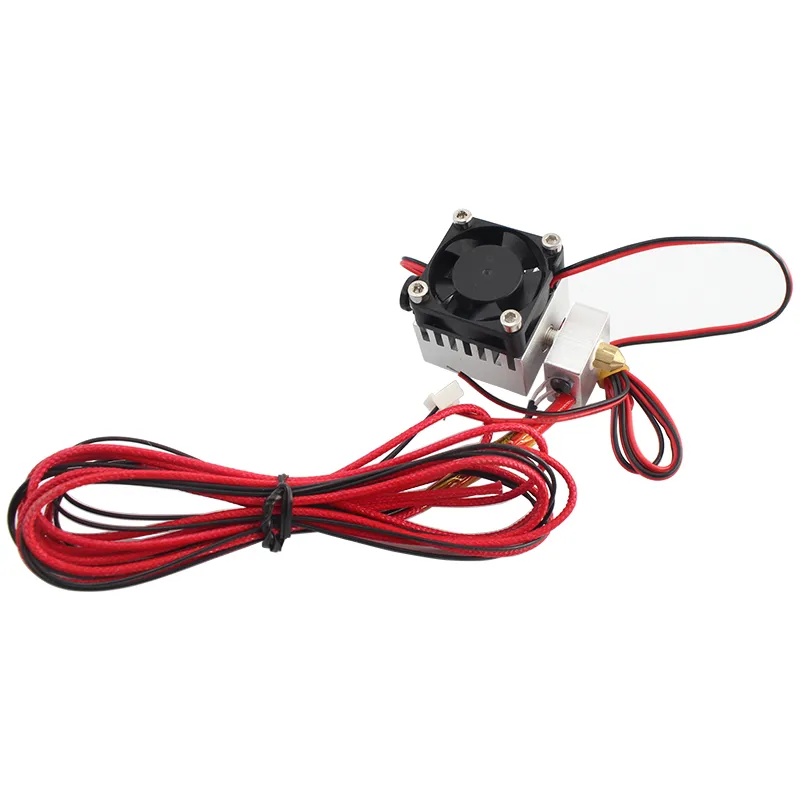

Wiring the tarantula extruder involves connecting the various electrical components, including the thermistor, heater cartridge, and stepper motor. Carefully review the wiring diagram provided with your design. Use appropriate gauge wires for the heating element and motor, and ensure all connections are secure and insulated to prevent short circuits. Pay close attention to polarity to prevent damage to the components. After wiring the extruder, use a multimeter to test the connections and verify the resistance of the thermistor and heating element. Properly wired electronics are essential for safe and reliable operation. Refer to online resources if any confusion arises.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is an integral part of building your own tarantula extruder. During the construction process or during its initial use, you might encounter several issues that require careful examination and resolution. Common problems include extruder jams, under-extrusion, over-extrusion, and temperature-related errors. Developing excellent troubleshooting skills will prove beneficial in maintaining and improving the extruder. Identify the cause of the issues before attempting to fix it. Refer to online resources, forums, and communities for assistance.
Common Issues and Solutions
Common issues include extruder jams, which are often caused by the filament getting stuck in the hot end. Solutions include clearing the jam with a cleaning rod or by disassembling the hot end. Under-extrusion, which results in gaps in your prints, could be the result of a clogged nozzle or incorrect temperature settings. Over-extrusion, on the other hand, may result in excess filament and requires temperature adjustments or calibration. Another common issue is temperature instability, which might indicate a faulty thermistor or problems with the heating element. Keep detailed records of problems and solutions so you have records to refer back to.
Maintenance and Care

Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity and optimal performance of your tarantula extruder. Consistent maintenance prevents breakdowns, extends the component’s life, and ensures consistently high-quality prints. Establish a regular maintenance schedule that includes tasks like cleaning, lubrication, and inspections. Regularly check the extruder for any signs of wear or damage. Early detection of any issues will help you avoid more serious problems. Following a maintenance schedule will minimize downtime and ensure the extruder operates efficiently.
Cleaning and Lubrication
Cleaning the extruder is crucial to remove any debris or filament residue that may affect its performance. Start by cleaning the nozzle, which can be done with a special nozzle cleaning tool. For the hot end, use a cleaning filament or perform a cold pull to remove any remaining material. Lubrication is critical for moving parts, like the extruder gears. Use a suitable lubricant sparingly to ensure smooth operation and to reduce friction. Don’t over-lubricate, as this may attract dust and debris. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and use lubricants specifically designed for 3D printing components.
Long-term Storage
When storing your tarantula extruder for an extended period, take specific precautions to protect it from damage and degradation. Remove the filament from the extruder to prevent it from degrading or causing a jam. Clean the extruder thoroughly, paying attention to all the small areas that might accumulate dust or debris. Store the extruder in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. If possible, store the extruder in a sealed container or bag to protect it from dust and moisture. These precautions will help maintain the extruder’s optimal condition.
Safety Precautions
Safety is paramount when working with any 3D printing equipment, especially when building and operating a tarantula extruder. Always unplug the extruder from the power source before performing any maintenance or repairs. The hot end can reach extremely high temperatures, so allow it to cool down completely before touching it to avoid burns. Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from any flying debris or molten plastic. Work in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhaling fumes from the heated plastic. Handle electrical components carefully, and ensure all connections are secure to prevent the risk of electric shock.
Building your own tarantula extruder is a rewarding project that allows you to gain a deeper understanding of 3D printing technology while also saving money and customizing your equipment. The journey may seem challenging, but by following these steps, you can successfully build and maintain your own extruder. Remember to stay organized, patient, and prioritize safety throughout the process.
