What is a Testia Tarantula
The Testia tarantula, while not a scientifically recognized species, is used here as a hypothetical case to explore tarantula characteristics and care. Tarantulas, in general, are large, hairy spiders belonging to the Theraphosidae family. These fascinating creatures are found in various habitats worldwide, captivating enthusiasts with their unique appearances and behaviors. Understanding the basics of tarantulas, even a hypothetical one like the Testia, is the first step toward appreciating their complexity and needs. These spiders are generally nocturnal hunters, and they play a vital role in their ecosystems by controlling insect populations. The diversity within the tarantula family is astounding, with species varying greatly in size, color, and temperament.
Appearance and Characteristics of Testia Tarantulas
Let’s imagine the Testia tarantula to have some distinct characteristics. This hypothetical tarantula would share common traits with real-world tarantulas but could also have some imagined unique features to make it stand out. The appearance of a tarantula is often the first thing that grabs your attention, so it is crucial to consider the features. Typically, tarantulas have a cephalothorax (fused head and thorax) and an abdomen covered in hairs. Their legs are long and covered in sensory hairs, assisting in movement and detecting vibrations. The chelicerae, or fangs, are located near their mouth and are used for injecting venom to subdue prey. The size and color of a Testia tarantula could vary widely depending on the hypothetical species or imagined characteristics.
Size and Physical Features
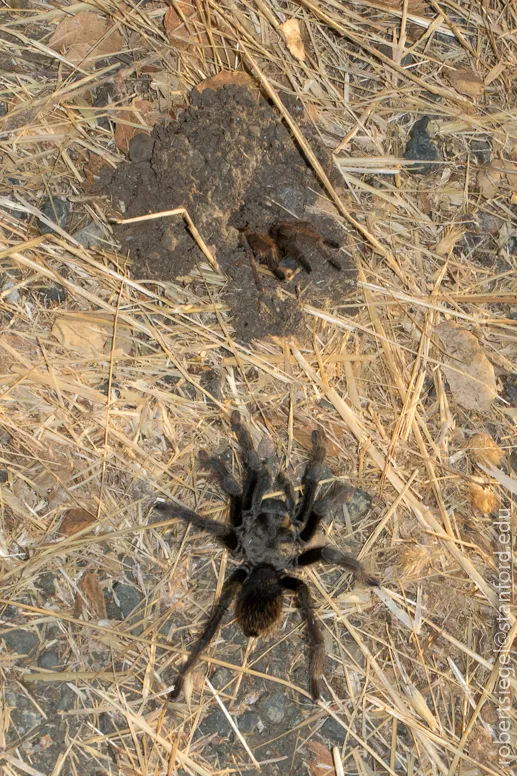

The size of a Testia tarantula would depend on the hypothetical species. Some tarantulas can have a leg span of over 10 inches, while others are much smaller. Consider that a Testia could be a medium-sized tarantula, perhaps with a leg span of 6-7 inches. The physical features would include the typical tarantula body plan the cephalothorax, abdomen, eight legs, and chelicerae. The body would be covered in hairs, which vary in length, density, and color. The hairs are crucial for sensory perception and defense. It is also important to consider the sensory organs, like the eyes and the sensory hairs that help detect movement and vibrations in their surroundings.
Color Variations and Patterns
The color of the Testia tarantula could vary greatly. Many real-world tarantulas display striking colors and patterns, ranging from solid blacks and browns to vibrant blues, oranges, and yellows. We can imagine the Testia tarantula to potentially have a unique color pattern, perhaps with contrasting bands or spots on its legs or abdomen. The coloration often serves as camouflage, allowing the tarantula to blend in with its environment. Consider that the colors might also play a role in attracting mates or deterring predators. The density and color of the hairs on the tarantula’s body can also change the overall appearance, contributing to the unique patterns and color variations.
Habitat and Distribution of Testia Tarantulas
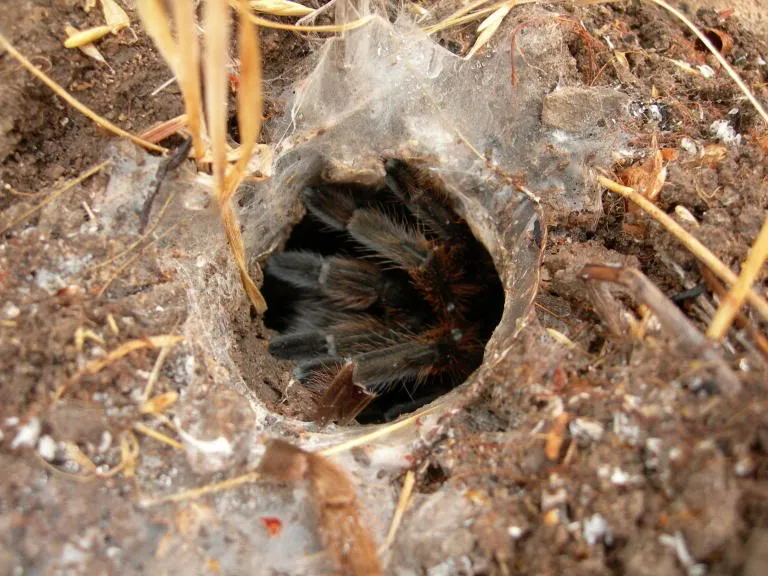
Imagining the habitat and distribution of a Testia tarantula is important, as it will influence many aspects of its behavior and needs. Tarantulas are found in a wide variety of habitats, including tropical rainforests, deserts, grasslands, and even suburban areas. The geographic distribution of a hypothetical Testia tarantula could be limited to a specific region. The habitat would be characterized by its climate, vegetation, and the availability of food and shelter. Understanding the natural environment provides clues about the tarantula’s needs and behaviors. The substrate, humidity, and temperature of the habitat play a key role in survival.
Where They Live and What They Prefer
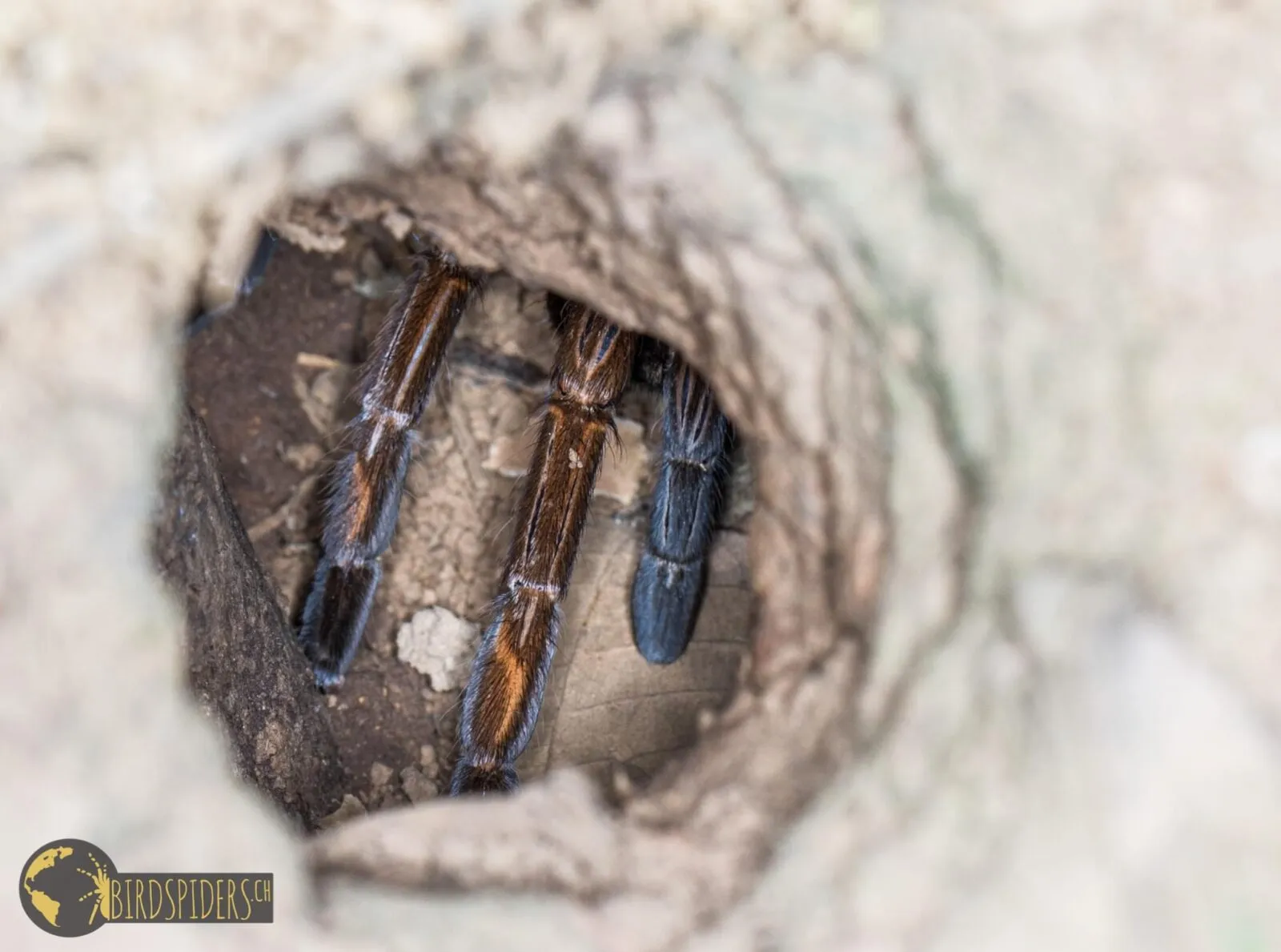

Testia tarantulas, in our imagination, might prefer a terrestrial lifestyle, living in burrows or under rocks. Some tarantula species are arboreal, living in trees, while others are fossorial, spending most of their time underground. The choice of habitat would depend on the tarantula’s size, temperament, and the availability of resources. The ideal environment would provide protection from predators, a stable climate, and access to food and water. A terrestrial Testia tarantula would likely need a burrow or a hide to feel secure. Considering the preferred type of habitat is critical when keeping a tarantula in captivity.
Natural Habitats and Ecosystems
The natural habitat of a Testia tarantula would likely consist of tropical or subtropical ecosystems. These environments offer suitable temperatures, humidity, and an abundance of insects for food. The Testia, within this ecosystem, would play a role as a predator. The presence of other animals, such as birds, snakes, and larger mammals, would influence the tarantula’s behavior and survival. Understanding the natural habitat allows us to replicate the conditions in captivity. The conservation status of tarantulas depends on habitat loss, pollution, and the illegal pet trade. Protecting their habitats is crucial for the survival of tarantulas.
Behavior and Lifestyle of Testia Tarantulas
The behavior and lifestyle of a Testia tarantula would be consistent with general tarantula behaviors. Tarantulas are generally solitary creatures, except during mating season. They are primarily nocturnal, active during the night, and they spend their days in burrows or under shelter. Understanding the behavior is crucial for providing adequate care. They are ambush predators, waiting for prey to come within striking distance. Tarantulas use their chelicerae to inject venom to paralyze their prey before feeding. They also have a defensive posture and are capable of biting and flicking urticating hairs as a defense mechanism against predators. The Testia tarantula, in our minds, is a fascinating creature with interesting behaviors that influence its survival.
Feeding Habits and Diet
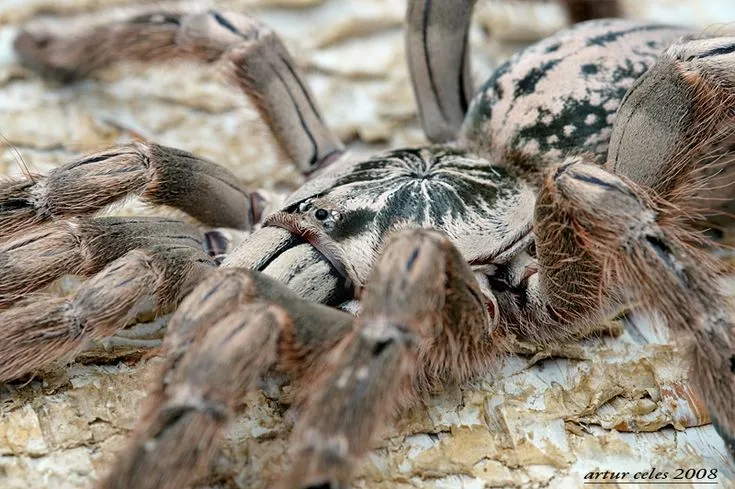

The diet of a Testia tarantula, and tarantulas in general, would consist primarily of insects. Crickets, roaches, mealworms, and other invertebrates make up the main part of the diet. The size and type of prey would depend on the size of the tarantula. Young tarantulas eat smaller insects, while adults can consume larger prey. Tarantulas have a unique way of eating. They inject digestive enzymes into their prey, breaking down the internal tissues before consuming it. This process is often messy. In captivity, the tarantula’s diet must be varied and supplemented with vitamins to ensure proper health. The feeding frequency depends on the size and age of the tarantula.
Predators and Defense Mechanisms
In its natural habitat, the Testia tarantula would face predators. Larger animals such as birds, snakes, and mammals, would pose a threat. Tarantulas have developed several defense mechanisms to survive. These mechanisms include hiding in burrows, biting, and flicking urticating hairs. These hairs irritate the skin and eyes of potential predators. The tarantula’s coloration provides camouflage, and their speed allows them to escape threats. In captivity, the tarantula is generally safe from predators. Understanding the defense mechanisms helps in providing a safe environment for the pet.
Interesting Facts about Testia Tarantulas
There are many interesting facts about tarantulas, and the Testia tarantula would be no exception. Here are some we could imagine: They have a lifespan that can range from several years to over 25 years, depending on the species and gender. Females typically live longer than males. Tarantulas can regenerate lost limbs, a remarkable ability. They molt regularly, shedding their exoskeleton to grow. Tarantulas do not require a lot of space and can survive long periods without food. These interesting facts make them fascinating pets. The diversity within the tarantula family is vast, with different species exhibiting unique adaptations and behaviors. The study of tarantulas provides valuable insights into the natural world.
Lifespan and Growth

The lifespan and growth of a Testia tarantula would follow a typical tarantula pattern. Females generally live much longer than males, sometimes exceeding 20 years. Males typically live for a few years after reaching maturity. Growth occurs through molting. During molting, the tarantula sheds its exoskeleton and grows a new one. Young tarantulas molt more frequently than adults. The frequency of molting decreases as they mature. The size of the tarantula increases with each molt. Providing proper nutrition and environmental conditions is crucial for healthy growth and a long lifespan. The molting process is a vulnerable time for the tarantula.
Conservation Status and Threats
The conservation status of real-world tarantulas varies depending on the species. Some species are considered vulnerable or endangered due to habitat loss, the pet trade, and pollution. If the Testia tarantula were a real species, its conservation status would need to be assessed. Threats to tarantulas include deforestation, urbanization, and climate change. The illegal pet trade poses a significant risk, as it can lead to over-collection from the wild. Conservation efforts are essential to protect these amazing creatures. Educating the public about the importance of tarantulas is key to promoting conservation.
Caring for Testia Tarantulas in Captivity
Caring for a Testia tarantula in captivity would be similar to caring for other tarantula species. Proper housing, temperature, humidity, and feeding are key to the tarantula’s health and well-being. The enclosure should be appropriate in size, allowing the tarantula to move and thrive. Maintaining the correct environmental conditions is critical. Handling the tarantula should be minimal and done with care. Careful handling would help to avoid stress or injury to the tarantula. The key elements of care for Testia and other tarantulas involve providing the correct environment and understanding their needs and behaviors.
Choosing the Right Enclosure
The right enclosure is a crucial aspect of tarantula care. For a Testia tarantula, the enclosure’s size should be appropriate to the tarantula’s size. It should be large enough for the tarantula to move and explore. The enclosure should be escape-proof and have adequate ventilation. Consider a glass or plastic terrarium with a secure lid. The substrate should be appropriate for the species and should allow the tarantula to burrow or hide. Decorations, such as hides, branches, and plants, can enhance the enclosure. The enclosure should be easy to clean and maintain.
Maintaining Temperature and Humidity
Maintaining the correct temperature and humidity levels is vital for the health of a Testia tarantula. The temperature should be appropriate for the species. A heat source, such as an under-tank heater or a heat lamp, may be needed to maintain the right temperature. The humidity level should be suitable for the species. Use a hygrometer to measure the humidity, and adjust the humidity by misting the enclosure or providing a water dish. Monitoring the temperature and humidity is essential for preventing health problems. Sudden changes in temperature and humidity can harm the tarantula. Research the specific requirements for your hypothetical Testia tarantula.
Feeding and Watering
Feeding and watering are essential parts of caring for a Testia tarantula. The tarantula should be fed an appropriate diet of insects, such as crickets and roaches. The size and frequency of feeding will depend on the tarantula’s size and age. Provide fresh water in a shallow dish at all times. Remove uneaten food and keep the enclosure clean. Overfeeding can lead to health problems. Observe the tarantula’s feeding habits to determine the appropriate amount of food. The tarantula will eat only when hungry. Providing the correct diet and hydration is the foundation of tarantula care.
Conclusion
While the Testia tarantula is hypothetical, this exploration has highlighted important aspects of tarantula care, behavior, and conservation. Understanding the needs of tarantulas, whether real or imagined, is crucial for providing proper care. This knowledge helps ensure the well-being of these incredible creatures and promotes a greater appreciation for their role in the ecosystem. Learning about tarantulas can also inspire a deeper understanding of the natural world. By exploring the world of tarantulas, we gain a new appreciation for biodiversity and the interconnectedness of all living things. Remember to always research and prioritize responsible pet ownership.
